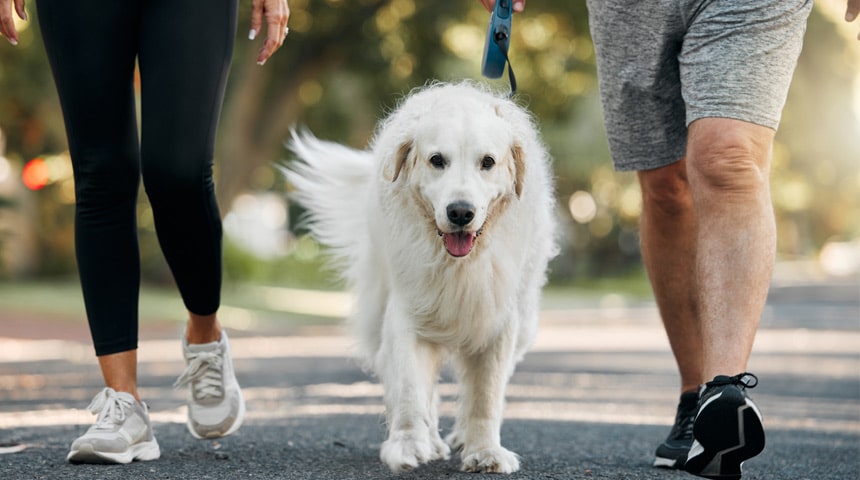
Obesity is a growing concern, with approximately 50-60% of pets in Canada classified as overweight or obese. In addition to increasing the risk of serious health issues such as diabetes, respiratory problems, and arthritis, obesity can also lead to chronic inflammation. This inflammation can worsen existing health conditions and contribute to the development of new ones, further compromising your pet’s overall well-being.
To help prevent obesity, it's essential to regulate your pet's food intake and encourage regular physical activity. One effective strategy for some pet owners is to use a scale to measure their pet’s total daily caloric intake in the morning. The daily amount is then divided into portions for breakfast and dinner, with a third portion set aside for treats throughout the day. If needed, consider low-calorie veterinary diets or enrolling in a specialized weight-loss program. Automated feeders can also be helpful in preventing overfeeding.
During your next veterinary visit, ask your vet to assess your pet’s body condition and recommend the appropriate daily calorie intake to help maintain or achieve a healthy weight. For additional guidance on ideal body weight, consult the resources provided.